Abstract
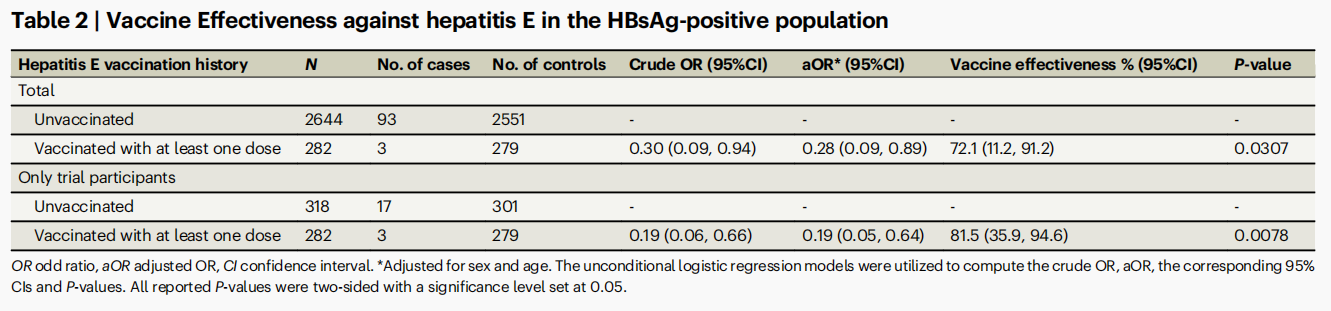
The effectiveness of the hepatitis E vaccine in high-risk groups, such as chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients, remains understudied. A key clinical manifestation of CHB is the persistent positivity of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). We conducted a test-negative design study involving 2,926 HBsAg-positive individuals (born 1941–1991; median age 49.0; male-to-female ratio of 1.4), identified through a hepatitis surveillance system, as part of the phase 3 trial (NCT01014845) of the recombinant hepatitis E vaccine HEV 239 (Hecolin). This system monitored suspected hepatitis cases and performed diagnoses across 11 townships in Dongtai, Jiangsu, China, from 2007 to 2017. Vaccine effectiveness of HEV 239 was assessed by comparing vaccination status between confirmed 96 hepatitis E cases and 2830 test-negative controls, using logistic regression adjusted for sex and age. We found that HEV 239 vaccination was associated with a reduced risk of hepatitis E among HBsAg-positive individuals, with an estimated effectiveness of 72.1% [95% confidence interval (CI) 11.2–91.2], and 81.5% (95% CI 35.9–94.6) among phase 3 trial participants. Our findings show that HEV 239 is highly effective in HBsAg-positive adults, supporting its future recommended use in this population.
Link:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-57021-3